Learn more about how LiDAR can help in your Airborne inspections below or contact us to discuss your inspection needs by calling us 479-365-3640 or filling out the form below.
What is LiDAR?
LiDAR or "Light detection and ranging" is the process of emitting a laser beam and measuring the amount of time it takes to strike an object and bounce back the emitter. Time is measured using the speed of light.
There are several types of airborne LiDAR sensors available, some that emit multiple pulse, creating several measured points along it’s vertical path. These laser beams are typically dispersed using a spinning or rotating mirror, creating a linear capture.
There are several types of airborne LiDAR sensors available, some that emit multiple pulse, creating several measured points along it’s vertical path. These laser beams are typically dispersed using a spinning or rotating mirror, creating a linear capture.
|
Airborne LiDAR Sensors
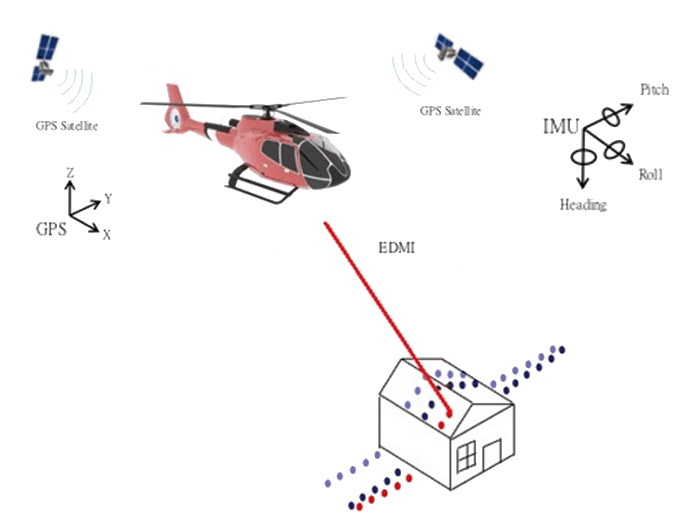
Exactly as during the photogrammetry process, the onboard GPS and the IMU record the details of the aircrafts position. The LiDAR solution adds an EDMI – Electronic Distance Measuring Instrument which measures along a path perpendicular to the flight path. Aerial LiDAR LiDAR measures points across the earth’s surface. The distance between consecutive measurements is referred to as point spacing or density. This density is a function of several variables: |
- The speed of the aircraft ~ The slower the speed the tighter the point spacing between rows of points perpendicular to the flight line.
- AGL – the altitude of the aircraft impacts the resulting density of the point cloud. A low elevation captures a higher density of points as the distance across the field of view is narrowed.
Airborne LiDAR Deliverables
Using LiDAR technology, we can provide a number of geospatial outputs such as point clouds, classified LiDAR and Digital Elevation Models. LiDAR also forms the basis for further analysis such as Thermal Line Rating and Utility Vegetation Management.
Using LiDAR technology, we can provide a number of geospatial outputs such as point clouds, classified LiDAR and Digital Elevation Models. LiDAR also forms the basis for further analysis such as Thermal Line Rating and Utility Vegetation Management.
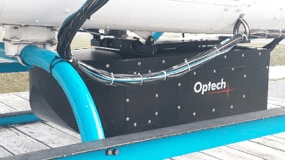
Optech Orion h300 Airborne LiDAR
FlyARH utilizes an Optech Orion H300 for airborne LiDAR inspections. During the acquisition, the onboard GPS (or GNSS) receiver accurately captures altitude, latitude and longitude coordinates of the LiDAR sensor. Simultaneously, the IMU is recording details on the attitude (pitch, yaw and roll) of the camera system at the instant of each image frame acquisition.
LiDAR for Utility Line Assessment
|
To mitigate fire risk and ensure regulatory compliance, utility companies worldwide are leveraging aerial inspection systems to monitor and inspect their geographically dispersed assets. Data is collected with sensors and analyzed to detect diseased trees that could fall and hit a powerline (fall ins) or trees that are encroaching on powerlines (grow ins).
|
Benefits:
- Easily map areas which are difficult to access, such as steep terrain, unstable slopes or wetlands.
- Assess pole height and lean while also capturing larger areas for accurate geotechnical data.
- By quickly identifying potential problems or at-risk assets, owners can address where safety concerns in the network are most urgent.
- Identify and map infrastructure obstructed by heavy vegetation. Penetrates tree canopies to deliver ground profiles in forested areas.
- Develop structure and line rating assessments.
- Monitor old and/or overloaded transmission lines by capturing line sag.
- Generate a complete 3D map of electric assets across a powerline and proposed powerline corridors.
- Generate digital surface models and bare earth models for site planning and drainage assessments.
- A key advantage to LiDAR surveys is their versatility. By collecting a rich data source up front, many needs can be served from one acquisition mission. Coordination of such interests leads to cost savings by investing in one rich data source.